What is Basal cell carcinoma?
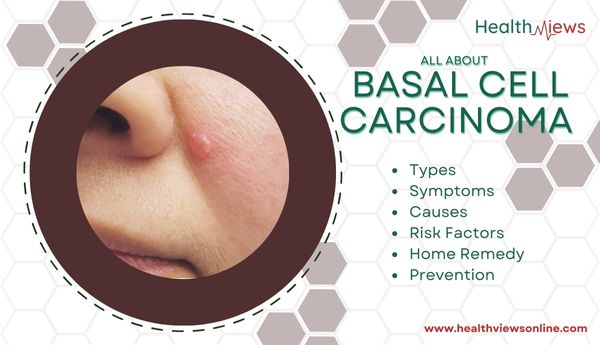
Basal cell carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that begins in the basal cells, which are skin cells that produce new skin cells as old ones die.
Basal cell carcinoma is most commonly seen as a slightly transparent bump on the skin, but it can also take other forms. Basal cell carcinoma is most common on sun-exposed areas of skin, such as your head and neck.
Long-term sun exposure is considered to be the primary cause of the majority of basal cell carcinomas. Applying sunscreen and avoiding the sun’s rays may help prevent basal cell cancer.
Also Read: All About Ringworm: Types, Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Home Remedy, Prevention
Types
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is classified into four types:
Nodular – The most common type of BCC is the nodular. Nodular BCC resembles a round pimple with visible blood vessels around it (telangiectasias).
Superficial spreading – It causes lesions that appear on your skin as small, shallow marks that are slightly lighter in color than the surrounding skin. These lesions develop on the trunk (torso), arms, and legs.
Sclerosing (morphea form) – These cancerous lesions resemble scars and grow slowly over time. This is the most common type on your face. This type may also appear as a small red dot on your skin.
Hyperpigmentation – When a region of your skin gets darker than the skin around it, is caused by this uncommon kind of BCC.
Causes
Basal cell carcinoma develops when one of the skin’s basal cells develops a DNA mutation. The epidermis is the skin’s top layer. The basal cell layer is the epidermis’s bottom layer. This layer’s cells are the ones that become cancerous in basal cancer. The majority of basal cell cancers develop on skin that is regularly exposed to sunlight or other forms of ultraviolet radiation.
The majority of cases of this kind of skin cancer occur in adults over 50. However, it can also happen to younger people who have spent a lot of time in the sun. Almost always, basal cell cancer has a modest growth rate. Rarely does it spread to different body parts. Source
Risk factors
These elements raise your chance of BCC:
- UV radiation from indoor tanning or the sun.
- Histories of skin cancer, such as melanoma or squamous cell carcinoma (SCC).
- Most BCCs develop in persons over the age of 50.
- Those who have fair skin are at higher risk.
- Men are more prone to get BCC than women.
- Burns, scars, and other skin problems can cause chronic infections and skin inflammation. Source
Symptoms
Basal cell carcinoma symptoms include:
- A wound or scar from acne
- Scaly skin, dry skin, a small wound, or a scar
- A sore or bump
- Skin that is dry and irritating, especially if it is red or pink
- A wart, mole, or any nonharmful growth.
- Freckle or age spot Source
Diagnosis
Your doctor or a dermatologist who specializes in skin diseases will perform a medical history and examination to evaluate any growths or changes in your skin.
Your doctor might do a skin biopsy, which entails taking a small sample of a lesion for laboratory analysis. This will show if you have skin cancer and what kind if any, you have.
Also Read: All About Cellulitis: Types, Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Home Remedy, Prevention
Treatment
The goal of basal cell carcinoma treatment is to completely remove cancer. Treatment may also be determined by whether this is a first-time or recurring basal cell carcinoma.
- Surgery is frequently used to treat basal cell carcinoma to completely remove the tumor and some surrounding healthy tissue.
Other therapies include:
- Radiation therapy
- Freezing
- Photodynamic therapy
- Targeted drug therapy
- Chemotherapy
When to see a doctor
If skin cancer is diagnosed, then the doctor will tell you
- What kind of BCC do you have?
- How far the cancer has spread (when possible tell)
Before deciding how to treat cancer, your dermatologist will carefully consider your health and the findings of the report.
Your doctor will perform a general physical exam and ask you questions about your medical history, skin changes, and any other signs or symptoms you’ve had.
Your doctor will look for other lesions on your body as well as suspicious areas on your skin Source
Prevention
Avoiding sun exposure from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m. and using sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher every day, especially in the winter, are the best ways to prevent skin cancer.
Additional preventive measures include:
- Once a month, examine your skin.
- Seeing a dermatologist once a year
- Using enough, the right kind, and frequently enough to be effective. Sunscreens should be broad spectrum, at least SPF 30, and waterproof to be effective. It should also be applied to all exposed skin areas and repeated every two hours or after swimming.
- Putting on protective clothing
Want to know about other skin disorders? Check out Skin Problems on Health Views Online.