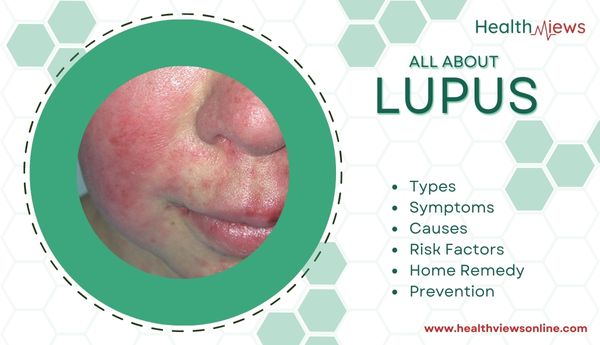
What is lupus?
The condition of lupus is brought on when your body’s immune system assaults its own tissues and organs (autoimmune disease). Lupus-related inflammation can impact a variety of body systems, including your joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, brain, heart, and lungs.
Internal organ issues such as rashes, sensitive skin, and joint discomfort are all signs of lupus (brain, lungs, kidneys, and heart). When symptoms are in remission, they may sometimes be slight or undetectable. Other times, the condition’s severe symptoms could make your daily life extremely difficult.
Types
They occur in various forms, including:
- Systemic lupus erythematosus: SLE is the most frequent type of lupus. SLE can induce acute or chronic inflammation of many organs or organ systems in the body. Source
- Cutaneous lupus (CLE): It affects only the skin, yet it can eventually progress to SLE in certain cases. create lesions or rashes, the majority of which will show up on skin exposed to the sun, such as the face, ears, neck, arms, and legs. Source
- Drug-induced lupus: A condition known as drug-induced lupus is brought on by specific prescription medications. Men are more likely to acquire drug-induced lupus than women because they receive these medications more frequently, but not everyone who takes them does. Source
- Neonatal lupus: It is an uncommon disorder caused by the mother’s anti-SSA/Ro and/or anti-SSB/La antibodies, which damage the fetus. The baby may have a skin rash, liver issues, or low blood cell counts after birth, but these symptoms usually go away after six months with no lasting damage. Source
Causes
It is an autoimmune disease in which your immune system assaults healthy tissue in your body. It is most likely caused by a combination of genetics and environment.
When a person develops an autoimmune disease, such as lupus, the immune system is unable to distinguish between harmful molecules, antigens, and healthy tissue. In error, the body misidentifies itself as foreign.
As a result, the immune system targets both healthy tissue and antigens with antibodies. Swelling, discomfort, and tissue damage result.
Risk factors
The following factors may raise your risk:
- Women are more likely to develop this skin problem.
- The skin disorder affects people of all ages, however, it is most commonly diagnosed between the ages of 15 and 45.
- Asian Americans, Hispanics, and African Americans are more likely to get this skin problem.
- People that have this or another autoimmune illness in their family
Also Read: All About Acne: Types, Symptoms, Causes, Prevention, Home Remedies
Symptoms
If you have lupus, you could suffer a wide range of symptoms. The symptoms differ from individual to person. Additionally, many of these symptoms are similar to those you can encounter from other medical disorders. One of the challenges in making a lupus diagnosis is this.
The symptoms can include:
- Joint discomfort.
- Muscle ache.
- Rashes.
- Fever.
- Sunlight sensitivity.
- Hair thinning.
- Sores in the mouth.
- Eyes that are dry.
- Fatigue.
- Chest ache.
- Stomach ache.
- Breathing difficulty.
- Swelling of the glands.
- Headaches.
- Confusion.
- Depression.
- Kidney, heart, or lung problems.
- Seizures.
- Clots form in the blood.
- Anaemia

Diagnosis
Due to its numerous symptoms, which are sometimes confused with those of other diseases, lupus can be challenging to diagnose. Many people have lupus for a long time before they realize they have it. Inform your doctor right once if you get lupus symptoms.
Lupus cannot be diagnosed by a single test. However, there are additional techniques for your doctor to determine if you have lupus, such as:
- Medical background
- Family history of autoimmune disorders like lupus.
- Full physical examination
- Urine and blood tests
- Kidney or skin biopsy
Treatment
Although there is no known cure for this problem, there are therapies that can make you feel better and less severe. Your treatment will be determined by your needs and symptoms.
It is treated by numerous different forms of medication. As your symptoms and requirements change, your doctors and nurses may alter the medication they prescribe for your lupus.
The main types of medicines are frequently used to treat lupus:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Corticosteroids
- Antimalarial drugs
- BLyS-specific inhibitors
- Immunosuppressive agents/chemotherapy
- Other medicines Source
Home remedies
- The active component of turmeric, curcumin, has shown potential for the treatment of autoimmune conditions like this skin problem.
- Ginger is an effective home cure for a variety of health issues, including this one.
- Health professionals believe that people with this skin problem lack hydrochloric acid, and consuming apple cider vinegar is one approach to supplement your body with it.
- One of the healthiest types of oil is coconut oil.
- Epsom salt helps the body better absorb magnesium and removes impurities.
- Holy basil or tulsi
- Flaxseeds are beneficial since they are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which help to reduce inflammation in lupus sufferers.
- Consumption of green tea Source
Prevention
Here are several factors that may minimize the risk of both the start of lupus and a flare-up in those who are at risk:
- Avoid direct sunlight.
- Some medicines can cause symptoms such as antibiotics melatonin and Rozerem, Septra, and Bactrim, so avoid them.
- Foods like garlic and alfalfa sprouts, as well as supplements like echinacea, can cause Lupus effectively
- Toxins like smoke, alcohol, and some other chemicals should be avoided. Source
Also Read: All About Ringworm: Types, Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Home Remedy, Prevention
Want to know about other skin disorders? Check out Skin Problems on Health Views Online.