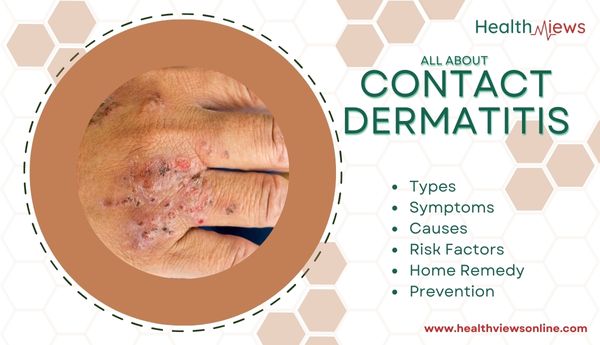
What is Contact Dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis is an itchy rash caused by an allergic reaction to a material or direct contact with it. Although the rash is not contagious, it can be extremely unpleasant.
The condition is widespread. We live in a world filled with allergens and irritants. If you have sensitive skin or other chronic skin conditions like atopic dermatitis, you might have contact dermatitis more frequently.
Many items, including cosmetics, scents, jewelry, and plants, might cause this reaction. The rash usually appears within a few days of being exposed.
Types
2 Types of Contact dermatitis exist:
- Allergic Contact dermatitis: It occurs when a substance to which you are allergic (allergen) causes an immunological response in your skin. It frequently just affects the area that was in contact with the allergen. This causes the body to release inflammatory chemicals, which can cause itchy and irritated skin.
Contact with the following substances is a common cause of allergic contact dermatitis:
- Jewellery made from nickel or gold
- Latex gloves
- Chemicals or fragrances in cosmetics and skincare items
- Poison oak or poison ivy Source
- Irritant Contact dermatitis: It is the most typical kind. When an irritant destroys the outer, protective layer of your skin, a non-allergic skin reaction takes place.
Irritant contact dermatitis can also arise when the skin comes into frequent touch with less irritating items, such as soap or even water.
People whose hands are frequently in touch with water, such as hairdressers, bartenders, and healthcare workers, are prone to irritation and contact dermatitis of the hands.
The following toxic chemicals can produce irritating contact dermatitis:
- battery acid
- bleach
- drain cleaners
- kerosene
- detergents
- pepper spray Source
Also Read: Actinic Keratosis: Types, Causes, Risk Factors, Prevention, Home Remedy, Facts
Causes
Contact dermatitis occurs when you are exposed to a substance that irritates your skin or causes an allergic reaction. The material could be one of the hundreds of thousands of known irritants and allergies. People frequently have both allergic and irritating reactions at the same time.
The following are typical causes of irritating contact dermatitis:
- Acids.
- Alkalis, such as drain cleaners.
- Urine and saliva are examples of bodily fluids.
- Poinsettias and peppers are examples of such plants.
- Hair coloring.
- Other solvents, such as nail polish remover.
- Varnishes and paints.
- Detergents or soaps that are too harsh.
- Resins, plastics, and epoxies are all types of resins.
Risk factors
Identifying the causes of your contact dermatitis is crucial to preventing reactions. These irritants and allergies occur most frequently:
- Nickel
- Occupational exposures
- Plants from the Toxicodendron family
- Cosmetics and personal care products
- Lotions and hair products
- Sunscreens and sunblocks
- Reactions to acrylic coatings on fingernails
- Topical antibiotics, such as Neosporin
- Anti-itch creams containing local anesthetics
- Oral and Dental Products
- Surgical Implant Devices
- Genetics Source
Symptoms
Contact dermatitis symptoms include:
- Skin that is red and inflamed
- Itching
- Swelling
- Bumps or blisters that are occasionally filled with clear fluid
- Skin that is hot or tender
These symptoms can range from moderate to severe, and they can emerge anywhere between a few hours and ten days following contact with the irritant or allergen. A contact dermatitis rash cannot be passed on to another person.
Diagnosis
By examining your symptoms and indications, your doctor may be able to determine if you have contact dermatitis. To find the root of your disease and learn more about the trigger chemical, you can be questioned. And a skin examination will probably be performed to evaluate the rash.
To determine what is causing your rash, your doctor might advise a patch test. This test may be helpful if the origin of your rash is unclear or if it flares up frequently.
Treatment
You might receive a prescription for medication from your doctor. Here are some observations:
- Creams or ointments containing steroids: These are administered to the skin to assist relieve rash symptoms. You could use topical steroids prescribed by your doctor, such as clobetasol or triamcinolone. Consult your doctor about how many times a day you should use it and for how long.
- Pills: In severe situations, your doctor may prescribe tablets that you swallow (oral drugs) to lower swelling, soothe itching, or combat a bacterial infection.
Home remedies
Try these self-care techniques to help soothe irritated skin and reduce itching:
- Avoid allergen or irritation products.
- Use an itch-relieving lotion or ointment.
- Use an anti-itch medication.
- Try a cool, moist compress.
- Don’t scratch. Cover an itching region with a dressing if you find it difficult to refrain from scratching it.
- Infuse the area with cool water and soak it.
- After washing, thoroughly rinse and gently dry your hands.
- Apply moisturizers all day long. Source
Prevention
To minimize your risk of developing contact dermatitis, follow these precautions:
- Avoid any substances that you suspect triggered the rash.
- Make a list of any new goods you’ve started using as well as any chemicals that frequently contact the affected parts of your skin.
- List all the prescription drugs and dietary supplements you take. Better still, bring the original containers as well as a list of the dosages and instructions. You should mention any creams or lotions you use.
- Cover metal fasteners close to your skin with an iron-on patch.
- Wear gloves or protective gear.
- Take precautions when near pets.
Want to know about other skin disorders? Check out Skin Problems on Health Views Online.