What are Warts?
Warts are infections of the skin caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). The infection develops hard, skin-colored pimples on the skin. Although warts are not normally hazardous, they can be unpleasant, possibly uncomfortable, and contagious. They can also be excruciatingly uncomfortable.
It differs in appearance and can appear alone or in clusters. Some are more prone to impact specific sections of the body than others. Warts are quite common, with nearly everyone affected at some point in their lives.
Types
It comes in five main categories. Each variety has a distinctive appearance and manifests on a different area of the body:
- Common Warts: They typically appear on the knees, the backs of your fingers and toes, and your skin. They can, however, show up elsewhere.
They may look thick, gritty, and rough, and have a rounded top. They might look like cauliflowers. Common warts frequently have darker skin than the surrounding tissue. Source
- Plantar Warts: They develop on the bottoms of the feet. Plantar warts, as compared to other types of warts, grow into your skin rather than out of it. Plantar warts can make walking difficult.
Two types of plantar can form on the sole:
- Myrmecial-type plantar warts
- Plantar warts with a mosaic pattern Source
- Flat warts: Juvenile warts, widely termed flat warts, typically appear on the face, thighs, or arms. The most common HPV kinds that cause them are 3, 10, and 28.
They are tiny and barely perceptible. A flat top gives flat warts the appearance of having been scraped. They come in a variety of colors, including yellow, pink, brown, and flesh. They frequently multiply in huge clusters of 20 to 200. Source
- Filiform warts: They appear around your mouth or nose, as well as on your neck and under your chin. They are contagious and have the potential to spread to other parts of your body.
Filiform warts are small and resemble a little flap or skin tag. They can appear as thin, finger-like strands on your skin. They are usually painless unless they occur in a sensitive part of your skin, such as a fold. Source
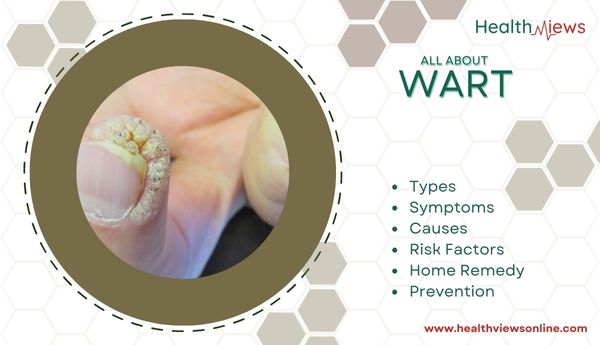
- Periungual warts: They develop beneath and around the toes and fingernails. They can be painful and have an impact on nail development.
They begin small, about the size of a pinprick, but can develop larger and spread to other regions via direct touch. They may be harsh to the touch and appear cauliflower-like. Source
Causes
The human papillomavirus infection is what causes warts (HPV).
The virus causes the top layer of skin to produce an abnormally large amount of keratin, a tough protein (epidermis). A wart’s rough, hard texture is due to the extra keratin.
However, the majority of types are transmitted by accidental skin contact or through shared items like towels or washcloths. The virus typically spreads through skin breaches, such as a scratch or a hangnail. They can also spread to your fingertips and the areas around your nails if you bite your nails. Source
Also Read: All About Genital Warts: Symptoms, Causes, Prevention, Facts
Risk factors
They can affect anyone, but some habits may increase your risk of getting them. These elements consist of:
- More common in children and teenagers.
- Sharing goods for personal hygiene
- Going barefoot in public bathrooms and swimming pools
- Biting one’s nails
- Immune system weakened
Additionally, touching meat can increase your risk of getting HPV.
Symptoms
The appearance varies. They might appear as follows:
- Dome-shaped.
- Flat.
- Rough.
- Brown, grey, black, or skin tone.
Diagnosis
Your doctor can identify warts only by looking at the bumps. Your doctor may occasionally perform a biopsy to obtain a sample of the skin growth for HPV testing.
Treatment
There are numerous wart treatments available. Nevertheless, no single treatment is 100% successful, and the wart could come back.
The goal of therapy is to get rid of the wart without leaving any scars or chance for it to come back.
Treatments include:
- salicylic acid
- cryotherapy
- chemical treatments
They frequently recur and require additional treatment, hence surgery is typically not advised to treat them.
Some treatments could have unwanted consequences including minor discomfort, blisters, and skin irritation near the wart. Source
Home remedies
Trying natural home remedies is another choice including:
- Apple Cider Vinegar
- Banana peel
- Garlic
- Orange peel
- Pineapple
- Potato
- Dandelion weed
- Aloe Vera
- Aspirin
- Clear nail polish
- Vitamin C and E
- Bee Propolis
- Castor oil
- Duct Tape
- Tea tree oil Source
Also Read: Garlic Health Benefits: Nutritional Facts, Value, Advantage, and Properties
Prevention
The following is what specialists advise to do to prevent acquiring warts:
- Avoiding touching a wart on another person
- Keeping personal care items separate
- Covering wounds and scratches
- Maintaining skin’s moisture
- Flip-flops in the locker rooms, swimming pools, and gyms
- Getting an HPV vaccine
- Treating excessive perspiration (excessive sweating)
Usually, warts disappear on their own. You can, however, take some actions to hasten the healing of your wart.
Want to know about other skin disorders? Check out Skin Problems on Health Views Online.